Funding Rate. How it works and how to capitalize on it

A funding rate is a fee designed to eliminate divergence in the derivative and asset price on the spot market.
On traditional exchanges, futures contracts used to have an expiration date (a forced execution date), which allowed market prices to be regulated. In the crypto industry, expiration has been replaced by funding, and contracts became open-ended. As a result, traders can keep their positions open indefinitely.
Funding rates are periodic payments paid by long traders to short traders. That is, the fee is paid not to the exchange, but to other market participants.
Funding rates help prevent long-lasting divergences in the spot price and the futures price of the asset. Exchanges usually recalculate the funding rate several times a day.
Funding rates are periodic payments paid by long traders to short traders. That is, the fee is paid not to the exchange, but to other market participants.
Funding rates help prevent long-lasting divergences in the spot price and the futures price of the asset. Exchanges usually recalculate the funding rate several times a day.
Standard funding rate is fixed at 0.01%
- When the funding rate is above 0%, the long position holders pay the short position holders.
- When the funding rate is below 0%, the short position holders pay the long position holders.
A high funding rate can either positively or negatively affect an open trade. A trader that pays a funding rate may suffer significant losses even in a low volatility market.
How to make money from funding rates?
In trading, the funding rate can be used similarly to the Fear and Greed Index, which gives buy signals when most traders are selling, and sell signals when greed is dominating the market.
Funding rates show which positions dominate the market at a certain point in time. If the funding rate is above 0.01%, it means that long traders are dominant. The rate below 0% indicates that short traders prevail.
Prices rarely meet most people's expectations, so funding rates can be used to gauge the market sentiment and take the opposite position. Note that high funding rates do not always cause prices to fall. In a bull market, for example, the funding rate is always high, in spite of the upward trend.
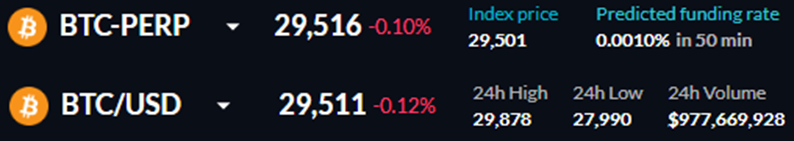
There are other, more sophisticated ways to make money from the funding rate. In the screenshot above, you can see that the bitcoin futures price trades higher than its spot price, and the funding rate is positive (long traders pay short traders). In this case, the trader can buy 1 BTC in the spot market and open a short position for an equivalent amount in the futures market. This scheme will allow the trader to profit from the funding rate and mitigate the risks of volatility. Holding a position open long enough, one can earn good funding fees.
Another option is to open long positions on stablecoins like USDT. As institutions hedge risk, there is often a negative funding rate in stable assets. At 5x leverage, such a position yields about 13% APY. While returns can be boosted by raising leverage, recent market events have shown that stablecoins are not that stable, and even with a seemingly safe position, they can get liquidated.
Although, on the one hand, it may seem quite easy to make money from the funding rate, these schemes require extensive background and a deep understanding of the market. It is always necessary to conduct a thorough investigation and calculate the risk/reward ratio.
Another option is to open long positions on stablecoins like USDT. As institutions hedge risk, there is often a negative funding rate in stable assets. At 5x leverage, such a position yields about 13% APY. While returns can be boosted by raising leverage, recent market events have shown that stablecoins are not that stable, and even with a seemingly safe position, they can get liquidated.
Although, on the one hand, it may seem quite easy to make money from the funding rate, these schemes require extensive background and a deep understanding of the market. It is always necessary to conduct a thorough investigation and calculate the risk/reward ratio.
Recommended

