Bitcoin Scalability Problem: Who’s Next in Line to Solve It?

While the Bitcoin blockchain is hailed as a benchmark for security and decentralization, its Achilles' heel remains its limited scalability. Despite Bitcoin Core’s strong defense against hacks, the ecosystem’s growth is constrained by the inherent limitations of Bitcoin Script.
Where there’s a challenge, there are always innovators ready to take it on. This holds true for BTC as well: the market is full of projects determined to scale the Bitcoin blockchain without sacrificing security. We explore some of the most ambitious newcomers.
And by the way, “scaling” and “scalability” are not the same thing. If you’re confused about the difference, we suggest reading our article on how St. Peter dealt with this particular issue.
BitcoinOS
BitcoinOS is a multi-layered platform built on Bitcoin, designed to accelerate transactions and expand network functionality without altering the Bitcoin core. The project also plans to integrate Zero-Knowledge Proof technology.
How It Works
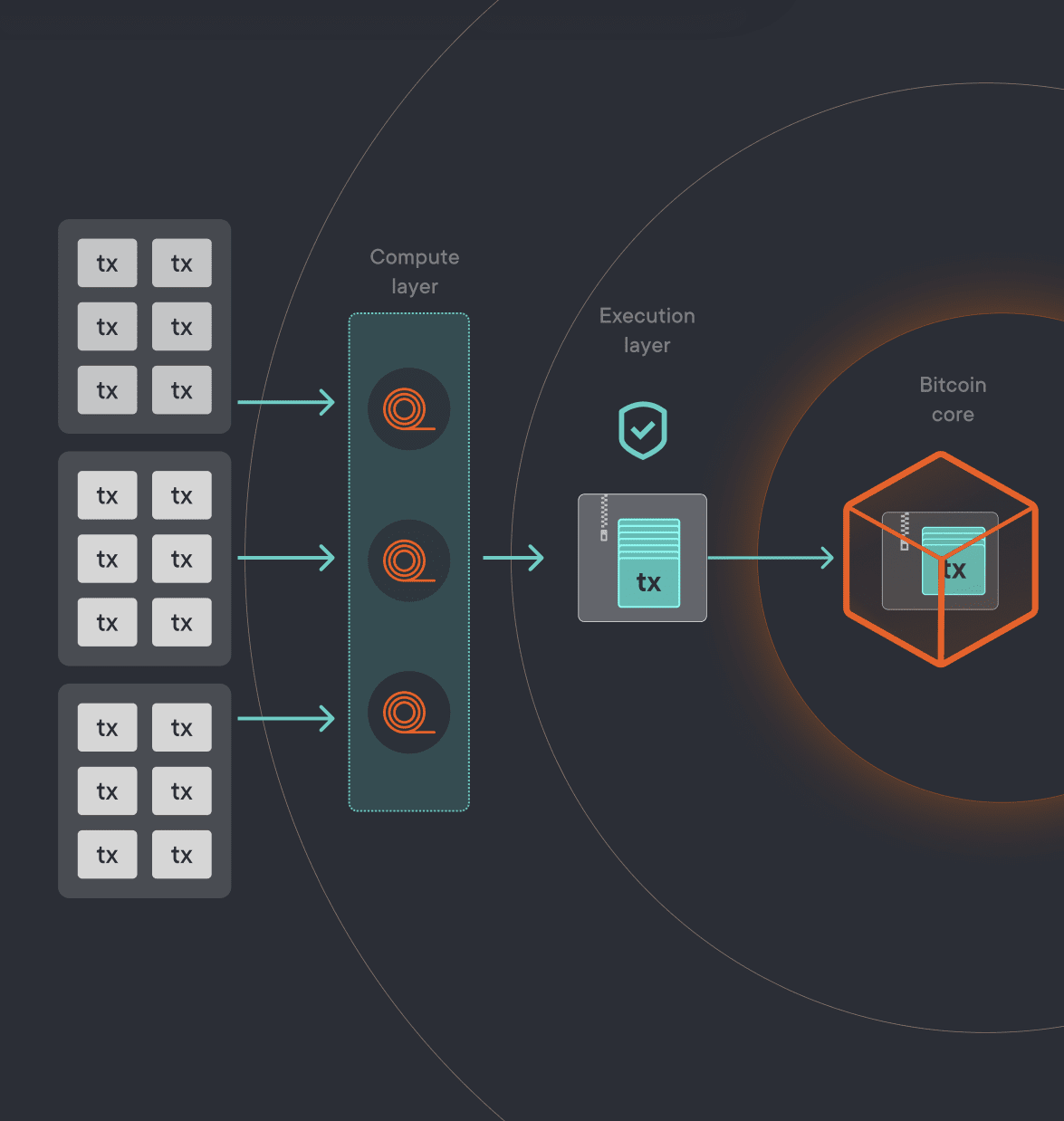
- Bitcoin Core (the base layer) remains unchanged, ensuring the secure storage and verification of transactions. Every block added to the blockchain becomes a permanent, immutable part of its history.
- The Execution Layer (second layer) is responsible for optimizing transactions. This layer introduces key differences from the main Bitcoin network. Here, the protocol can bundle small transactions into larger ones, reducing fees and increasing processing speed. Additionally, this layer is expected to serve as a bridge between various applications running on the third layer.
- The Compute Layer (third layer) is where smart contracts are created and executed, allowing for the deployment of third-party decentralized applications (dApps) that can interact with one another.
This layered architecture enables developers to choose the best tools and programming languages for building their applications within the BitcoinOS ecosystem.

BitcoinOS Structure. Source: sovryn.com
Advantages of BitcoinOS
- Enhanced Scalability: Bundling transactions improves scalability and boosts network capacity.
- Smart Contract Support: The ability to create smart contracts opens up a broader range of applications that can be built on the Bitcoin blockchain.
- Security and Stability: Preserving the integrity of the Bitcoin Core code ensures the protocol’s security and resilience.
BitcoinOS Roadmap
Following its launch, the team outlined several key goals in their roadmap:
- Introduce an execution environment compatible with the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) to support complex financial instruments like perpetual contracts;
- Develop features to enhance transaction privacy;
- Launch the SOV token, which will grant holders voting rights on project decisions.
Disadvantages of BitcoinOS
BitcoinOS faces significant competition, as many L2 solutions have emerged in recent years, with developers enhancing Bitcoin’s smart contract functionality to rival leading ecosystems like Stacks, Rootstock, Internet Computer, and the Lightning Network.
This means BitcoinOS will need to differentiate itself clearly to succeed, and it remains to be seen what specific advantages it will leverage to stand out in this competitive landscape.
Fractal
Fractal is a sidechain network built on top of the Bitcoin blockchain, designed to increase the network’s throughput without sacrificing security.
How It Works
- Like BitcoinOS, Fractal is built on Bitcoin Core, ensuring the original code remains intact.
- Fractal enables the creation of multiple sidechains branching off from the main blockchain, each capable of processing data independently. This approach is aimed at significantly enhancing the overall network capacity.
- These sidechains are created when the main chain reaches its maximum capacity.
- Transactions are then redirected to the sidechain with the lowest current load.
- Ultimately, all transactions on these sidechains are recorded on the Bitcoin mainnet, ensuring robust security.
In simple terms, the Fractal protocol acts like a traffic controller on a busy highway. When traffic (transactions) slows down and threatens to cause a jam, an alternate route is opened to divert some of the traffic. However, the final destination (recording data in Bitcoin Core) remains unchanged for all transactions.

Fractal routes some transactions to sidechains. Source: fractal-bitcoin.notion
Advantages of Fractal
- Fractal is compatible with new digital asset standards like Ordinals and BRC-20.
- By reactivating the OP_CAT code (a part of the Bitcoin protocol that was disabled in 2011 due to high memory requirements), Fractal enables the execution of smart contracts.
- The network’s throughput adjusts automatically based on current demand, a feature referred to as “dynamic scaling.”
It's important to note the mining function. Like Bitcoin, Fractal uses the Proof-of-Work (PoW) consensus algorithm, which requires node operators to contribute computing power to create new blocks. Miners are rewarded with FB (Fractal Bitcoin) tokens, which are used for transaction fees, ecosystem governance, and access to nodes and services. A key advantage is that miners can use their existing mining equipment (ASICs or GPUs), which lowers the entry barrier for new participants.
Fractal introduces Cadence Mining, a hybrid model that combines solo and pool mining to balance decentralization and security. In this system, two out of every three blocks are mined individually, while one is mined in a pool. This setup helps maintain the network’s security by leveraging the efforts of both BTC and FB miners.
Disadvantages of Fractal
There are some concerns, such as the absence of a roadmap on the official website. Additionally, it's unclear whether Fractal is connected to the Fractal ID startup, which experienced a major data breach on July 14, 2024. Given that the Fractal Mainnet was only recently launched (on September 9, 2024), this possibility cannot be entirely dismissed.
Recommended

