EOS Cryptocurrency Reviewed

The EOS blockchain platform and cryptocurrency represent the rare success story of an unknown asset transitioning from an ICO to a modern ecosystem, complete with asset tokenization, smart contracts, and a decentralized application development environment.
Introducing another contender in the "Ethereum killer" category. The main goal of the network's creators was to significantly improve its throughput and transactions per second (TPS). The founders of EOS were optimistic that their new, optimized network could gain market share from Ethereum, NEO, and Cardano by offering users an excellent alternative with fast, inexpensive transactions and a scalable solution (notably, Ethereum was still using the cumbersome PoW algorithm at the time).
The EOS network is an open-source blockchain platform focused on high performance, flexibility, and security. By utilizing the EOS virtual machine and the high-performance WebAssembly (WASM) engine, the network enables the creation of smart contracts and decentralized applications (dApps) that can process nearly instantaneous transactions with minimal fees (no more than 10 cents equivalent).
EOS blockchain employs a Delegated Proof-of-Stake (DPoS) consensus algorithm, allowing the crypto community to elect network validators and oversee their performance. Thanks to this decentralized format, the network is never controlled by a limited group of stakeholders and belongs to the entire EOS community, which democratically elects or replaces validators. Of course, mining is not an option with this consensus algorithm, but passive income can be earned through staking.
The EOS network is interesting due to its implementation of modern technologies (smart contracts, dApps, etc.) and its native coin with a similar name. Over the years, a community has formed around the project, allowing members to participate directly in its future development through a decentralized autonomous organization (DAO).
EOS currently ranks 45th on Coinmarketcap in terms of market capitalization, totaling nearly $1.3 billion. Daily trading volumes consistently remain above $100-150 million.
The Creation of EOS
The idea to create EOS emerged in the summer of 2017, conceived by Daniel Larimer. He is known in the crypto community for his previous projects, BitShares and Steemit. Larimer decided to fund the creation of EOS through an Initial Coin Offering (ICO). The fundraising period lasted from June 26, 2017, to June 1, 2018 (341 days), during which the network operated in test mode.
The technical development of the project was carried out by block.one, a company registered in the Cayman Islands. Larimer held the position of CTO within the firm. The developers focused on creating support for parallel processing and asynchronous communication in the EOS network. This enabled a significant increase in TPS performance.
On June 10, 2018, the first block was created on the EOS network. From that moment, the EOS network began operating in a production environment.
EOS Network Foundation
On August 25, 2021, EOS stakeholders reached an agreement on funding the project and created a separate organization named the EOS Network Foundation (ENF), founded by Yves La Rose.
The ENF is a nonprofit organization that coordinates both financial and non-financial support for the EOS project. It also oversees network development and encourages initiatives within the community. Acting as the central hub of the EOS network, the ENF leverages decentralization to bring about positive changes to the project, both in the present and the future.
Community-driven EOS
The EOS project is managed by the crypto community through a decentralized autonomous organization (DAO). Any member can propose changes or upgrades, which are then voted on by all EOS coin holders. This approach encourages community members to generate ideas and demonstrate leadership qualities, inspiring developers to enhance the project and network.
The ENF has funded various working groups that focus on improving the EOS ecosystem, including core infrastructure, API, SDK, DeFi, and security aspects.
Where to buy, store, and trade EOS?
EOS is supported by a significant number of wallets in various formats. Most of the wallets that support Ether also provide support for EOS.
For example, you can store EOS on wallets like:
- Mobile wallets: Jaxx, Anchor Wallet, Token Pocket, Wombat, and others
- Desktop wallets: SimpleEOS, GreyMass EOS, Scatter EOS, Guarda, Ethereum Wallet, Jaxx, Exodus, Anchor Wallet, and others
- Hardware wallets: Ledger Nano S, Trezor
A wide variety of wallets, in different formats, support the EOS coin. Most wallets compatible with Ether also support EOS. For example, EOS can be stored using:
- Mobile wallets: Jaxx, Anchor Wallet, Token Pocket, Wombat, and more.
- Desktop wallets: SimpleEOS, GreyMass EOS, Scatter EOS, Guarda, Ethereum Wallet, Jaxx, Exodus, Anchor Wallet, and more.
- Hardware wallets: Ledger Nano S, Trezor.
It was initially anticipated that EOS coins would become available on various exchanges right after the ICO. However, the first listings only began towards the end of 2017. Today, EOS can be purchased on the most popular centralized trading platforms and marketplaces. While you can store EOS on these platforms, it's crucial to choose an exchange carefully.
EOS can be bought and traded on many leading CEX exchanges, including Binance, Coinbase, OKX, Huobi, Kraken, WhiteBIT, HitBTC, Kucoin, Bybit, Crypto.com, Gate, Bitfinex, Poloniex, MEXC, Newdex, AscendEX, Bithumb, and others.
EOS Coin
The EOS coin is the native asset of the EOS blockchain, offering its holders several benefits:
- A fast and secure method for exchanging and transferring funds.
- The opportunity to participate in the growth of the EOS network and Web3 technologies.
- Access to all resources and services within the EOS ecosystem.
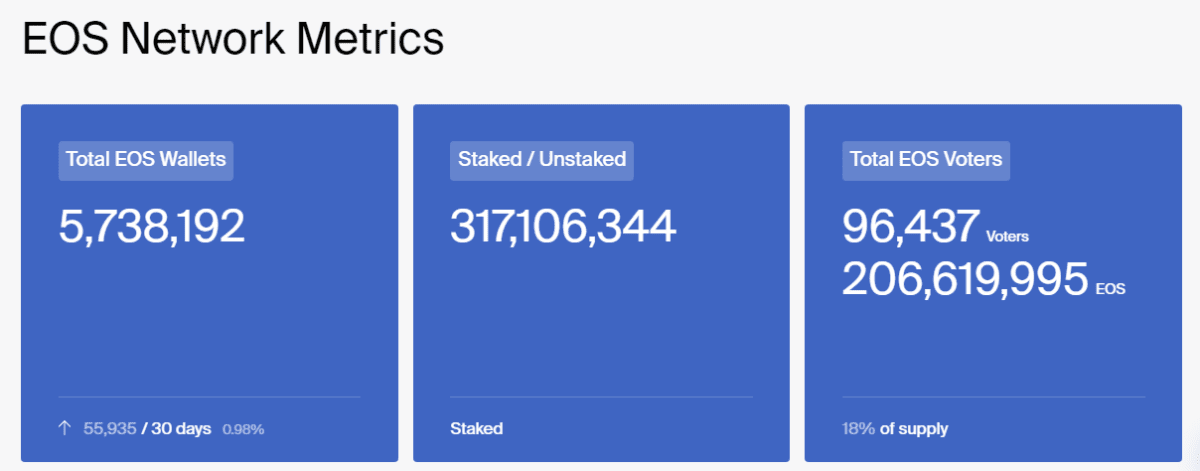
Currently, over 1.083 billion EOS coins have been issued. There is no emission limit to combat inflation. Nearly 6 million active wallets exist, with more than 317 million EOS staked. Over 206 million coins grant almost 100,000 holders the right to vote on network and project changes.
EOS Future Prospects
Seasoned market players are aware that Dan Larimer, the creator of EOS, has a less-than-stellar reputation. He failed to complete his two previous projects, BitShares and Steemit. However, Larimer claims that he considered the mistakes of his earlier ventures when creating the EOS platform and does not plan to repeat them.
The recently established venture company, EOS Network Ventures (ENV), is prepared to invest in projects built on EOS. ENV aims to provide these projects with initial strategic capital and assets for growth. Investments will primarily target technology startups in the Web3 sector, with a focus on GameFi, metaverses, esports, NFTs, and fintech services. Therefore, we can expect positive news about the expansion of the EOS ecosystem in the future.
Recommended

